
The administrative theory of management focuses on the principles that could be used by managers to coordinate the internal activities of organizations. The most eminent of the theoreticians of administration was Henri Fayol. Fayol observed a work stoppage and judged it to be a failure of management. He believed that organizational management practices are important in fostering predictability and efficiency in organizations.
The administrative theory of management focuses on the principles that could be used by managers to coordinate the internal activities of organizations. The most eminent of the theoreticians of administration was Henri Fayol. Fayol observed a work stoppage and judged it to be a failure of management. He believed that organizational management practices are important in fostering predictability and efficiency in organizations.
While proponents of scientific management developed principles that could help individual workers perform their tasks more efficiently, administrative theory focused on principles that could be used by managers to coordinate the internal activities of organizations. The most eminent of the theoreticians of administration was Henri Fayol.
Henri Fayol (1849-1925), was a French industrialist and an eminent European management theorist. Henri Fayol is known as the father of management and he developed a general management theory and also established the 14 management principles. Fayol was unknown to American managers and scholars until his most important work, “General and Industrial Management”, was translated into English in 1949. These 14 management principles are used to run an organization and are beneficial for forecasting. , planning, decision making. , organization and management, control and coordination of processes.
“Everyone needs some notion of management; at home, in government affairs, the need for managerial ability is commensurate with the importance of the business, and for individuals, the need is everywhere more in agreement with the position occupied”.
Administrative management
Many managerial concepts that form the foundation of modern managerial thought were first articulated by Fayol. Fayol believed that with scientific predictions and proper management methods, predictable satisfying results were sure to follow. The theory falls under the administrative management school of thought (as opposed to the scientific management school headed by Fredrick Taylor).
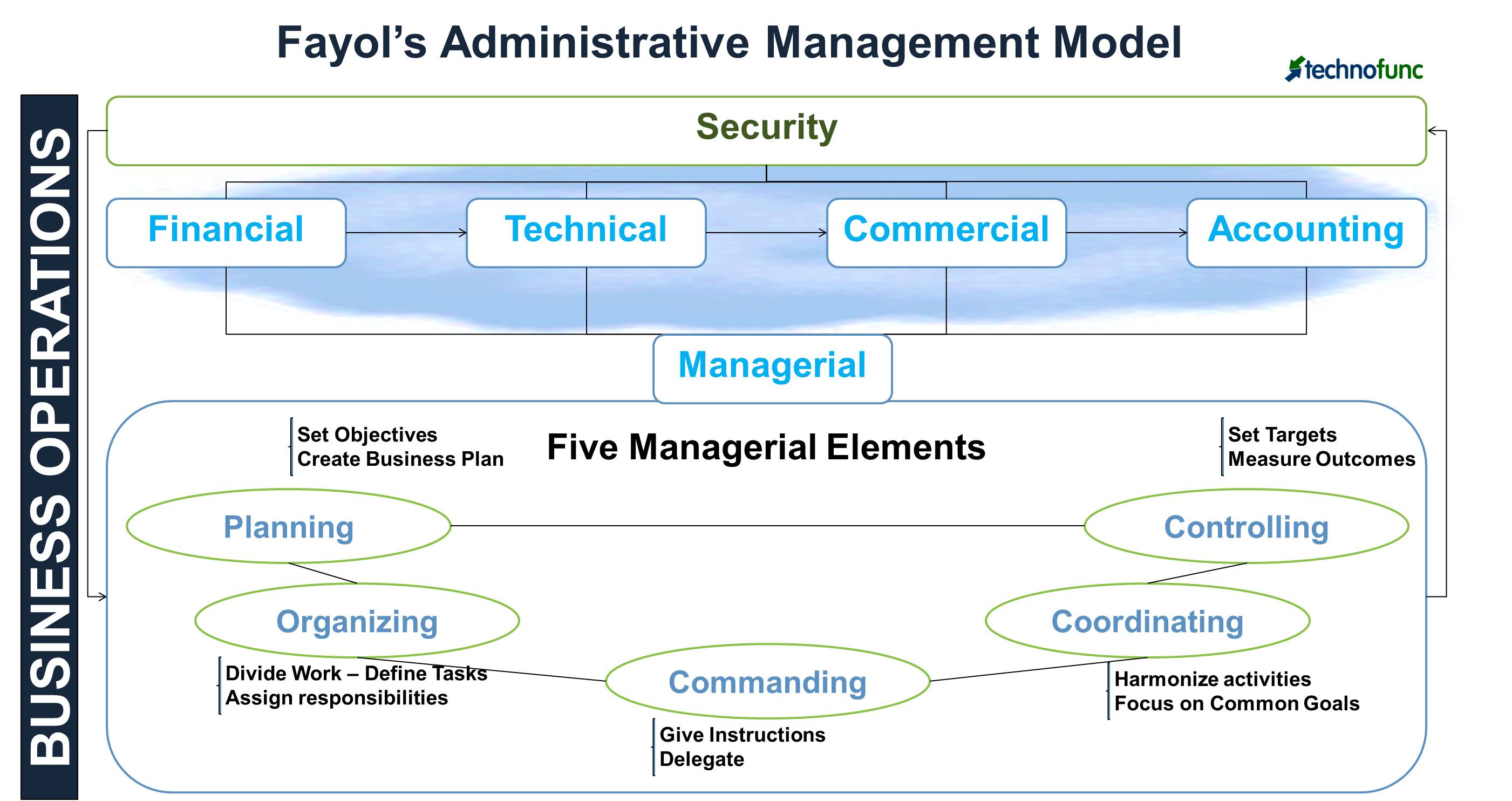
According to Fayol, an organization’s business operations could be divided into six major activities.
- Technical: Production and manufacturing products
- Commercial: Purchase, sale and exchange
- Financial: Search for an optimal use of capital
- Security: Protect employees and assets
- Accounting: Recording and inventory of costs, profits, liabilities, keeping balance sheets and compiling statistics
- ManagerialPlan, organize, command, coordinate and control
Fayol’s Five Elements of Management
Fayol’s studies have mainly focused on the last activity which is “Managerial Activity”. He identified five major elements of management that outline the expected behaviors that managers should adopt to effectively achieve the business goals of the organization. The five elements of management are:
- Planning
- Organization
- commanding officer
- Coordination
- Control
Let’s briefly discuss these five elements of management as described by Fayol and relevant to modern businesses and managers even today.
1. Planning:
Planning is the most important management function. This is a forward-looking exercise in creating a business plan, determining the different steps for executing and monitoring the plan, and defining the technology and resources needed to implement the plan. Planning involves identifying in advance what needs to be done, how it will be done, and what the deadlines and responsibilities for execution are. It sets the roadmap from the current state of the organization to where the organization wants to be. The output of the planning function is logical goals and their timelines. Managers need to engage in short and long term planning.
2. Organization:
Once an action plan is designed, managers have visibility of what is expected and when. To achieve these milestones, they need to find resources and assign them appropriate tasks. They should focus on providing everything needed to complete the plan; Including raw materials, machinery and tools, capital, funds and human resources. They must identify and establish the responsibilities of each of the departments or divisions, and specify the organizational relationships.
3. Order:
Managers must implement the plan using the allocated resources efficiently. They need to understand the strengths/weaknesses of their workforce and the limitations of available resources. Managers must lead and motivate employees to achieve organizational goals. Employees may need appropriate resource allocation and an effective support system and supervision. Directing requires exceptional interpersonal skills and the ability to motivate and inspire people while balancing personnel and production needs.
4. Coordination:
Organizations are interdependent systems and need coordination across different departments to stay in sync and on plan. The greatest responsibility of the manager is to “align” all the activities required in the different functions in order to facilitate and ensure the success of the organization according to the agreed plan. Managers need good communication skills to ensure that the coordination mechanism works effectively. Managers are needed to synchronize elements of the organization and must consider the delegation of authority and responsibility and the span of control within units.
5. Control:
The last element of management as described by Fayol involves the comparison of staff activities to the action plan. This is the monitoring and evaluation component of management. The control function guarantees that the tasks have been carried out with the required quality in all areas and helps to detect possible deviations from the plan of the organization. This ensures quality performance with respect to business objectives and satisfactory results while maintaining an orderly and trouble-free environment. Control includes information management, performance measurement and the implementation of corrective actions.
Relevance in the Modern Workplace
Fayol believed that management practices were the key to the predictability and effectiveness of organizations. Fayol’s five managerial functions are clearly similar to modern managerial functions – planning, organizing, staffing and controlling. Fayol’s concept of management forms the cornerstone of contemporary management theory. Many of Fayol’s practices are still alive in today’s workplace. These elements can be found in modern organizations in several ways: as accepted practices in certain industries, as reworked versions of original principles or elements, or as remnants of organizational history to which practices and philosophies alternatives are offered. The new manager in the digital age must acquire the latest leadership and management skills to succeed in today’s competitive world.
Suggested Readings and Resources
Related links
You May Also Like Management Theories | Modern Approaches to Management | Quantitative Theory of Management | Taylor Scientific Management | Principles of management by Fayol | Management concept | Behavioral approach to management
Creation date Sunday, August 23, 2020 Hits 72339
