The “Record to Report” process, also known as “Account to Report” or simply General Ledger process, refers to the maintenance of general ledger law from the recording of transactions to the preparation of trial balances for the transaction. unit and consolidated financial results of the reporting company.
Bookkeeping is an essential accounting activity that provides the solid financial foundation on which an organization rests. The accuracy and integrity of the financial statements an organization produces largely depend on the accuracy and integrity of its record keeping activities. Entering journals and reviewing and posting to ledgers are the two main bookkeeping activities. Logs are where all transactions are first recorded on a daily basis. Information from a journal is then recorded in ledgers to update each account. Various accounts in the ledgers are then summarized, tested and validated, and used to produce financial statements at the end of an accounting period.
Here we will help you understand basic accounting concepts and introduce you to the process of entering journals, reviewing, summarizing entries, reconciling, and finally reporting and closing an accounting period. This section of will help you understand the fundamentals of an effective automated general ledger system and the concepts explain all the important GLs including how to analyze a transaction, post it to the appropriate journal, and then view it in great books. We assure you this is the best place to learn the registration process to report!!
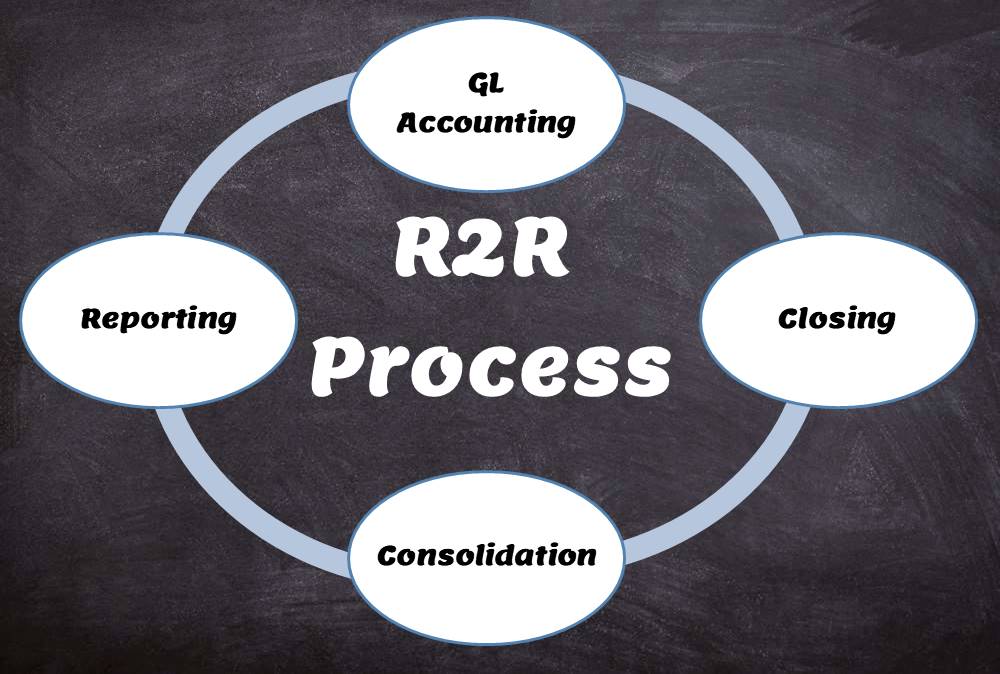
Record to report (R2R) is a financial and accounting management process that involves the collection, processing, analysis, validation, organization and ultimately reporting of accurate financial data. The R2R process provides strategic, financial and operational feedback on the organization’s performance to inform management and external stakeholders. The R2R process also covers the stages of preparation and reporting of global accounts.

The purpose of the general ledger is to sort transaction information into meaningful categories and charts of accounts. The general ledger sorts information from the general journal and converts it into account balances and this process converts the data into the information needed to prepare financial statements. This article explains what a general ledger is and some of its main features.
What is a General Ledger? The general ledger (also known in accounting as the general ledger or nominal ledger) is the heart of any accounting system. A general ledger is the master set of accounts that summarize all transactions made within an entity. Ledger is the skillful grouping and presentation of log entries. Learn the basics of accounting, the general ledger process, and the general ledger flow.

Accounting is a process designed to capture the economic impact of daily transactions. Every day, many events and activities occur in an entity, these events and activities are in the normal course of business; However, each of these events may or may not have an economic impact. Events or activities that have an effect on the accounting equation are accounting events.
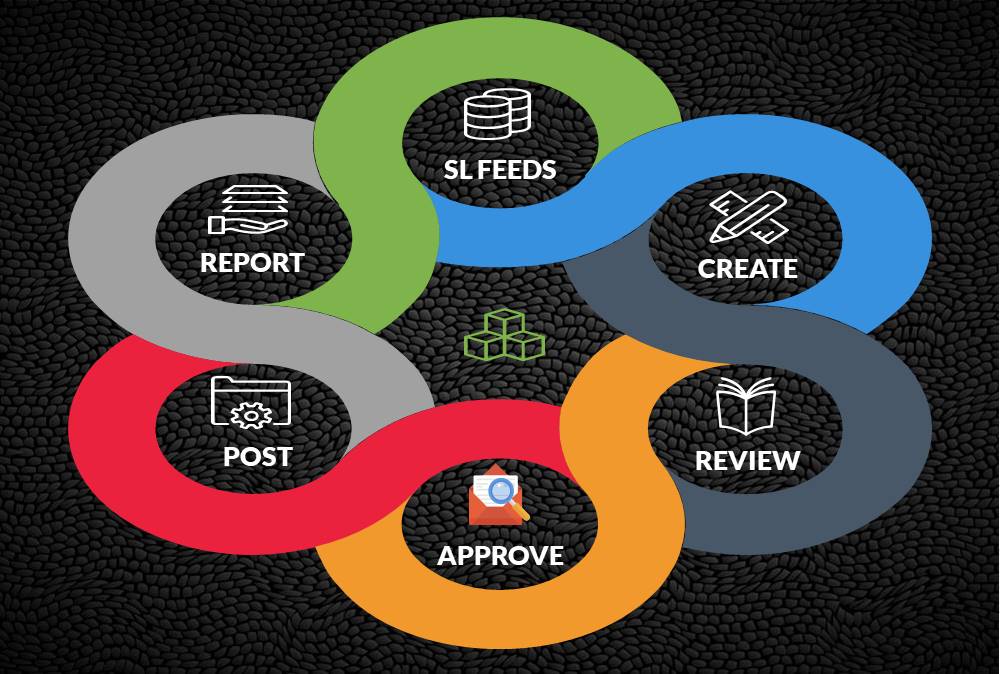
In this article, we’ll explain the general ledger journal processing flow, from entering journals to running final financial reports. Understand the generic general ledger process flow as it occurs in automated ERP systems. The accounting cycle explains the flow of converting raw accounting data into financial information while the general ledger process flow explains how journals flow through the system.

Although technically a general ledger seems to be quite simple compared to other processes, in large organizations the general ledger has to provide a lot of functionality and it becomes considerably larger and more complex. Modern business organizations are complex, manage multiple lines of products and services, rely on a large number of registered legal entities, and have varied reporting needs.

The general ledger is the central repository of all accounting information in an automated accounting world. Summarized data from various sub-ledgers is published in GL, which eventually helps in the creation of financial reports. Learn more to understand the role and benefits of an effective general ledger system in automated accounting systems and ERPs.

There are five main account types to capture any accounting transaction. Besides these fundamental accounts, some other special purpose accounts are used to ensure the integrity of financial transactions. Some examples of such accounts are clearing accounts, suspense accounts, contra accounts, and intercompany accounts. Understand the importance and use of these accounts.

Generally, general ledger accounts are classified into five categories within a chart of accounts. Double-entry bookkeeping uses five and only five types of accounts to record all transactions that can possibly be recorded in any accounting system. These five accounts are the foundation of any accounting system, whether it is a manual or automated accounting system. These five categories are assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses.
