
Action Centered Leadership is a model developed by John Adair and focuses on the three responsibilities of a leader which are task completion, team management, and individual management. All of these action items are mutually dependent and important to any leader.
John Eric Adair is a British leadership theorist and author of over forty books. His “Action-Centered Leadership Model” is based on “Functional Leadership Theory” and is used for many leadership learning courses. Adair’s ideas became very popular because they challenged the leadership traits and theories of great men and were very practical and relevant for managers to experience and in a variety of work environments.
Principles of Functional Theory
Functional theory addresses the specific behaviors of leaders that should contribute the most to organizational effectiveness by focusing on how the leadership process occurs. The leader must ensure that all the needs of the group are taken into account.
- Functional leadership theory was given by Hackman & Walton, 1986; McGrath, 1962
- Addresses specific leader behaviors that contribute to organizational effectiveness
- Leadership is based on a set of group behaviors that get things done
- Believes that the main job of the leader is to provide for the needs of the group
- The leader is effective if he contributes to the effectiveness and cohesion of the group
- Any member of the group can perform this set of behaviors
Action-centered leadership model
The action-centered leadership model is developed by focusing on what leaders do and is based on the following principles:
- The task can only be done by the team rather than a single person/leader
- The team will only excel when all members are fully developed
- Members should be motivated and up to the challenge of the task
- Leadership can be taught; if one person can do something, then others can also learn to do it
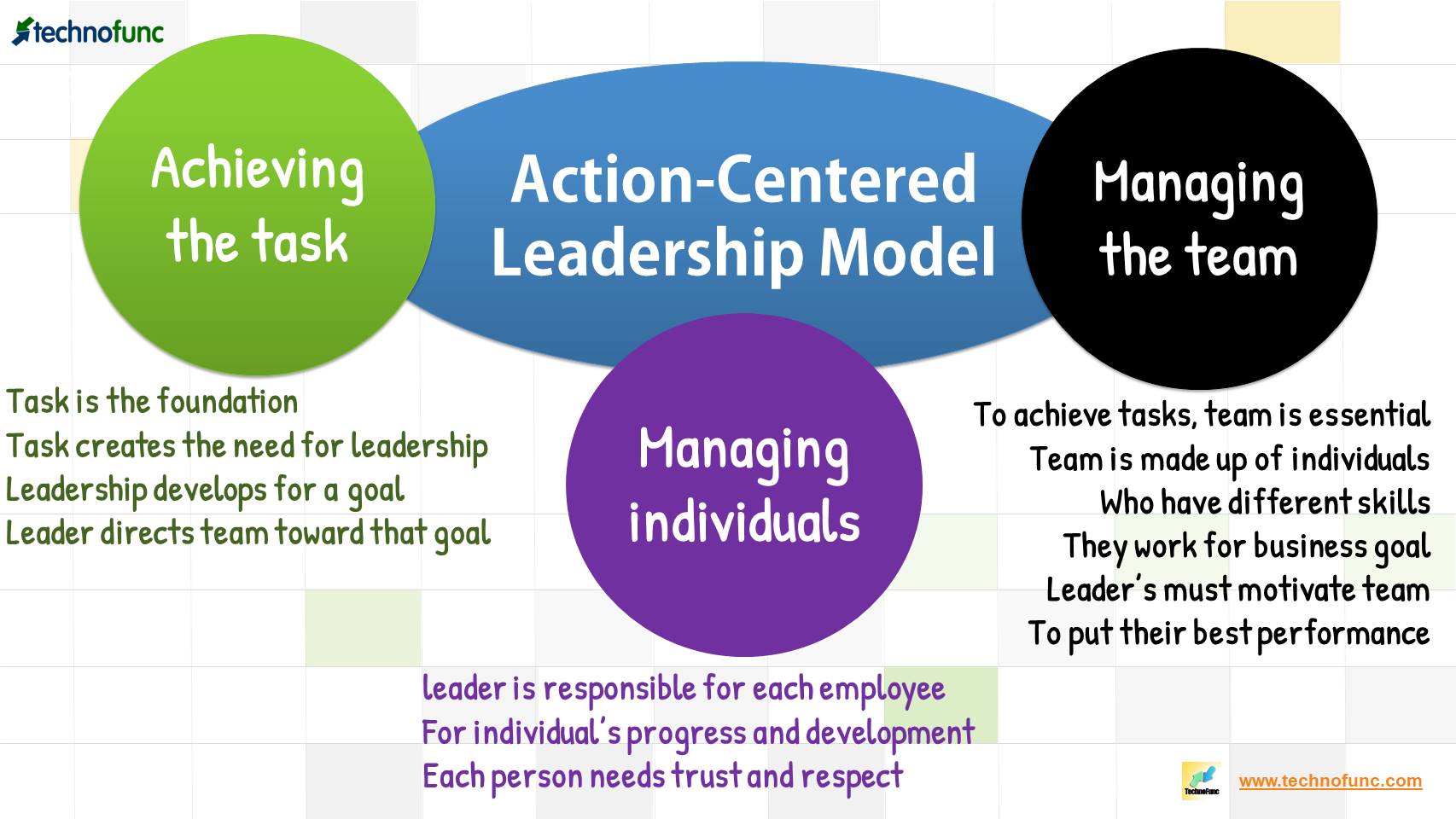
Adair’s business model can be represented by Adair’s Three Circles Diagram {The Three Circles are a trademark of John Adair}, which illustrates his three main management responsibilities. Each of these three elements plays an important role in leadership, and only when all three are properly balanced will the leader be successful and effective:
1. Complete the task: The task is the foundation that creates the need for leadership. Without the task, there is no need for leadership. Every leadership role is developed because there is a goal in mind and someone needs to be responsible for leading the team towards that goal.
2. Manage the team or group: To carry out the tasks, the team is essential. The team is made up of individuals with different skills and backgrounds, and they collectively contribute to the company’s goal. The primary responsibility of a leader is to motivate team members to do their best to achieve the best possible performance in the task.
3. Manage/empower individuals: The leader is responsible for each employee, their progress and development. Forgetting individuals as humans and treating them only as a resource that must do what is best for the organization is a serious leadership mistake. Getting the most out of each team member means treating them with trust and respect as the individuals they are. Each individual needs recognition through pay, enjoyment, challenging work and responsibility.
The eight functions of leadership
John Adair has prescribed the following key functions for team leaders and says they are important to the action-centered leadership model:
- Defining the Task: Setting Clear Goals with SMART Goals
- Planning: finding information, defining tasks after consulting the substitutes
- Initiation – Team briefing and division of tasks
- Control: get maximum results with minimum resources
- Evaluate: Assessing performance and ways to improve
- Motivating: Rewards and Incentives
- Organization: time management, personal development and delegation
- Lead by example: do what I do
What is Adair’s action-centered leadership model?
Adair’s business model can be represented by Adair’s three-circle diagram, which illustrates his three main management responsibilities. The main responsibilities of a leader are to get the job done by managing individuals and groups. It offers an integrated approach to group management and facilitation.
What is John Adair’s theory?
The action-centered leadership theory is proposed by John Adair and has become very popular due to its simplicity. By understanding the interaction between the task, the team and the individual and focusing on these elements, a leader can achieve success and effectiveness.
What is functional and action-oriented leadership?
The “Action-Centered Leadership Model” is based on “Functional Leadership Theory” and is used for many leadership learning courses. Functional theory addresses the specific behaviors of leaders that should contribute the most to organizational effectiveness by focusing on how the leadership process occurs. The leader must ensure that all the needs of the group are taken into account. It offers an integrated approach to group management and facilitation. A leader must focus on completing tasks by managing individuals and groups.
What type of leadership meets the needs of the work team and the individual?
Action-centered leadership relates to the needs of the work team and the individual. According to John Adair’s theory of action, leadership does not depend on the characteristics of a person but is something that can be learned. The action-centered leadership model is easy to apply and maintain. Leaders must be able to focus on the basics of team development, increasing productivity, improving the quality of work, and delivering strong results.
Related links
You May Also Like Functional Leadership Theory | Environment Approach | Open Systems Model | Leadership role theory | Sociotechnical systems | Contingency theories of leadership | Leadership Life Cycle Theory | Situational theories of leadership | The Great Man Theory | Approach by leadership skills | McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y | Social learning theories | Leader Member Exchange Theory | Lewin’s change management model | Four Factor Leadership Theory | Multi-linking model | Normative theory of leadership | Vroom’s Expectancy Theory | Fiedler’s leadership model | Participatory leadership theories | Leader-Participation Model | Strategic contingencies | Cognitive Resource Theory | Transactional theory of leadership | Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs | Reciprocal influence approach | Idiosyncrasy Theory Credit | Social Identity Theory | Transactional Analysis | Transformational Theories of Leadership | Burns Transformational Leadership Theory | The systemic approach to leadership | Self-leadership | Servant Leadership | Motivation-Hygiene Theory | Behavioral approach to management | Behavioral theories of leadership | Katz’s Three Skills Approach | Charismatic theory
